Impact from the evolution of private vehicle fleet composition on traffic related emissions in the small-medium automotive city
Abstract
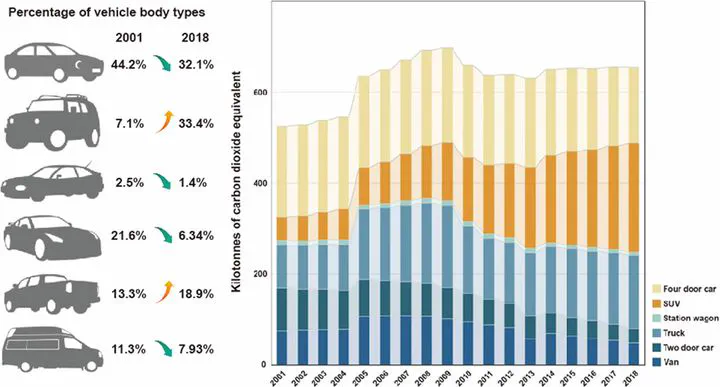
Understanding the emission characteristics in the evolution of private vehicle fleet composition has become a key issue to be addressed to develop appropriate emission mitigation strategies in transportation sector. In this study, the influence of such evolution on on-road emissions was investigated based on a comprehensive dataset encompassing vehicle fleet composition, demographic, economic, and energy features from a representative small-medium automotive city in North America. The decoupling analysis was carried out to assess the dynamic linkage between environmental pressure exerted by the transportation sector and economic growth at both city level and national level in North America. We also developed an approach that supports the long-term traffic-related air pollutant prediction and investigated the potential influence on urban air quality. A sharp upward trajectory was observed in the quantity of SUVs from 2001 to 2018, gradually replacing the dominance of the quantity of four-door cars. There was a significant shift in the GHG emissions emitted from vehicle types used for passenger transport that emissions from SUVs and trucks rose by 374.0% and 69.3%, respectively, whereas emissions from four-door cars, two-door cars, station wagons, and vans all decreased. The changes in vehicle composition, along with the steady trend in GHG emissions from private fleet and decrease in on-road air pollutant concentrations found in Regina, were a response to the establishment of federal fuel economy standards and improved fuel economy. Relative decoupling was observed in aggregate for Regina and Canada in most of the years while both experienced economic downturns and increases in environmental pressure in the form of emissions from 2014 to 2015. The predicted results also demonstrate the high capability of XGboost machine learning algorithm in predicting on-road air pollutant concentrations of CO, PM2.5, and NOX.
Type
Publication
Science of The Total Environment